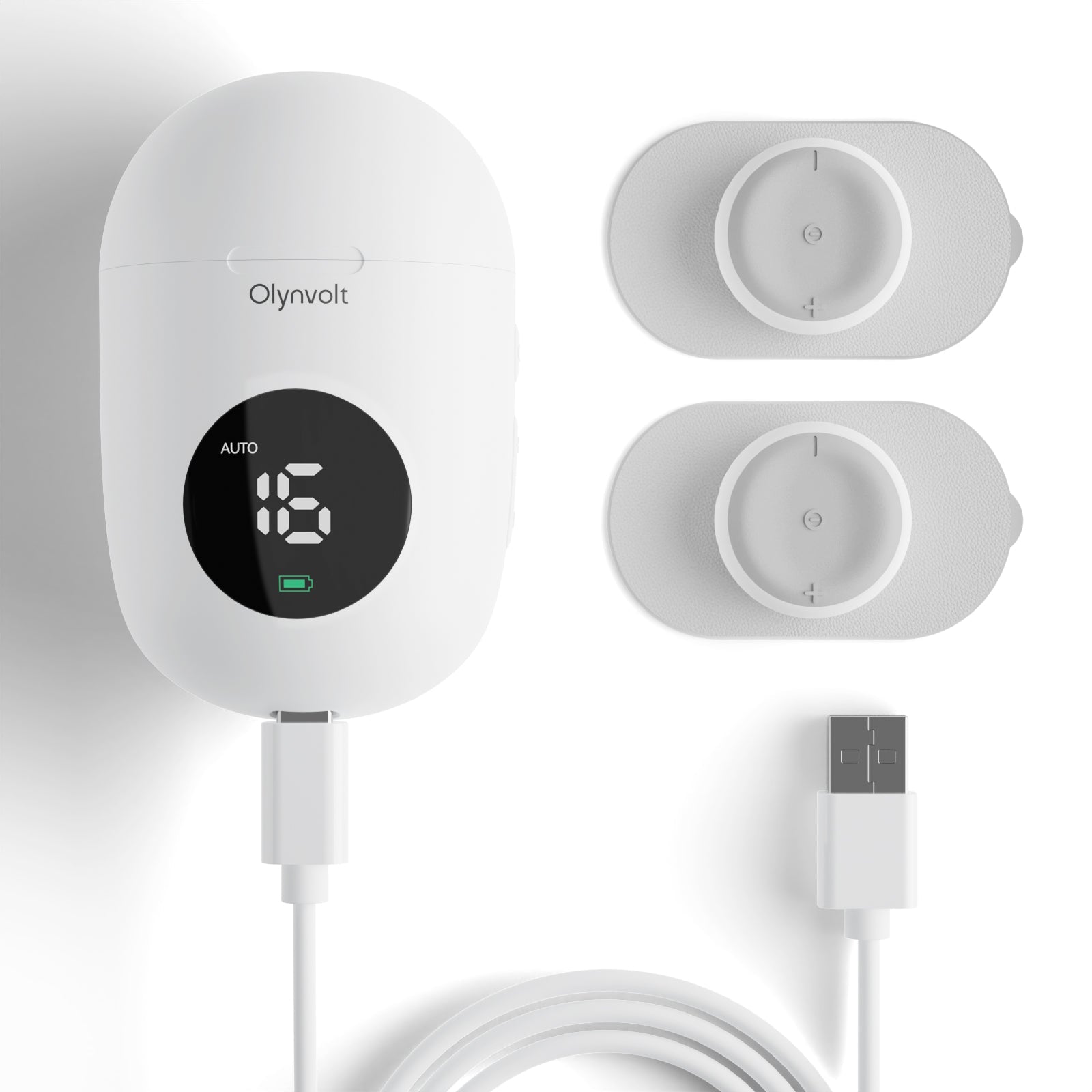
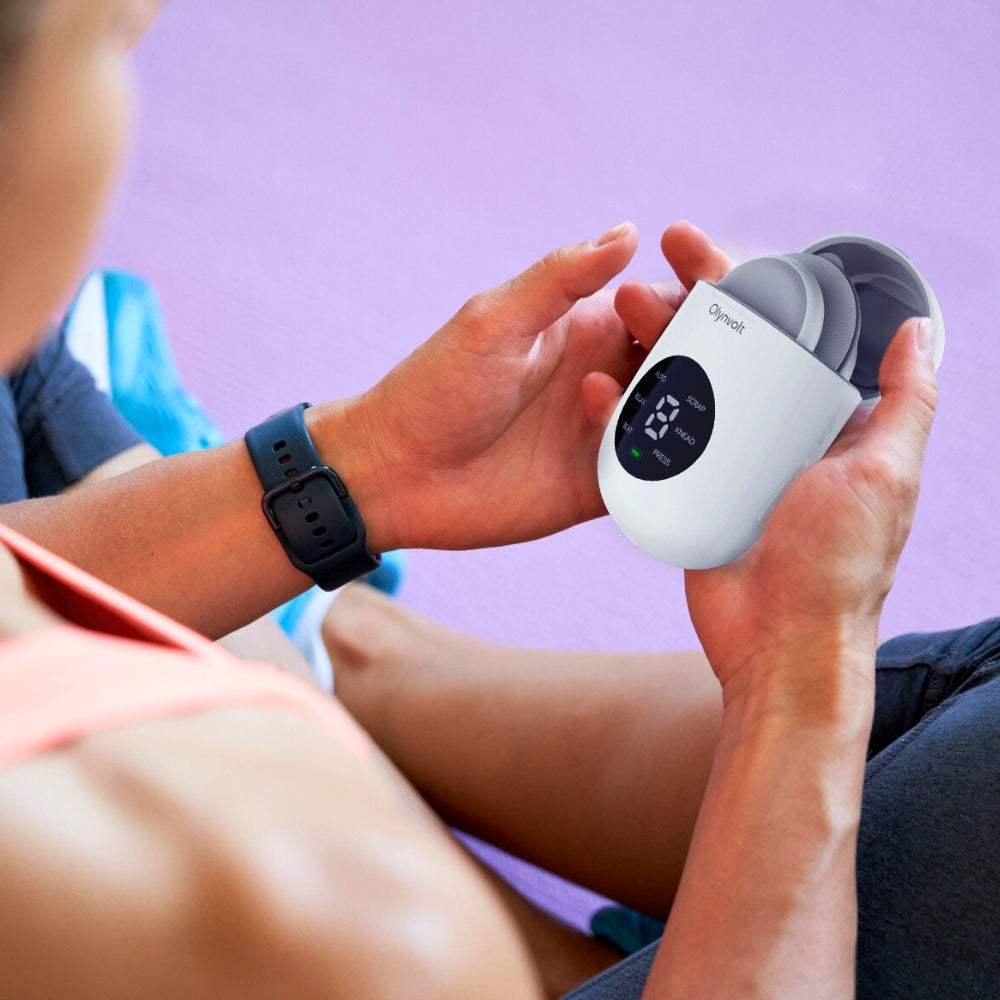
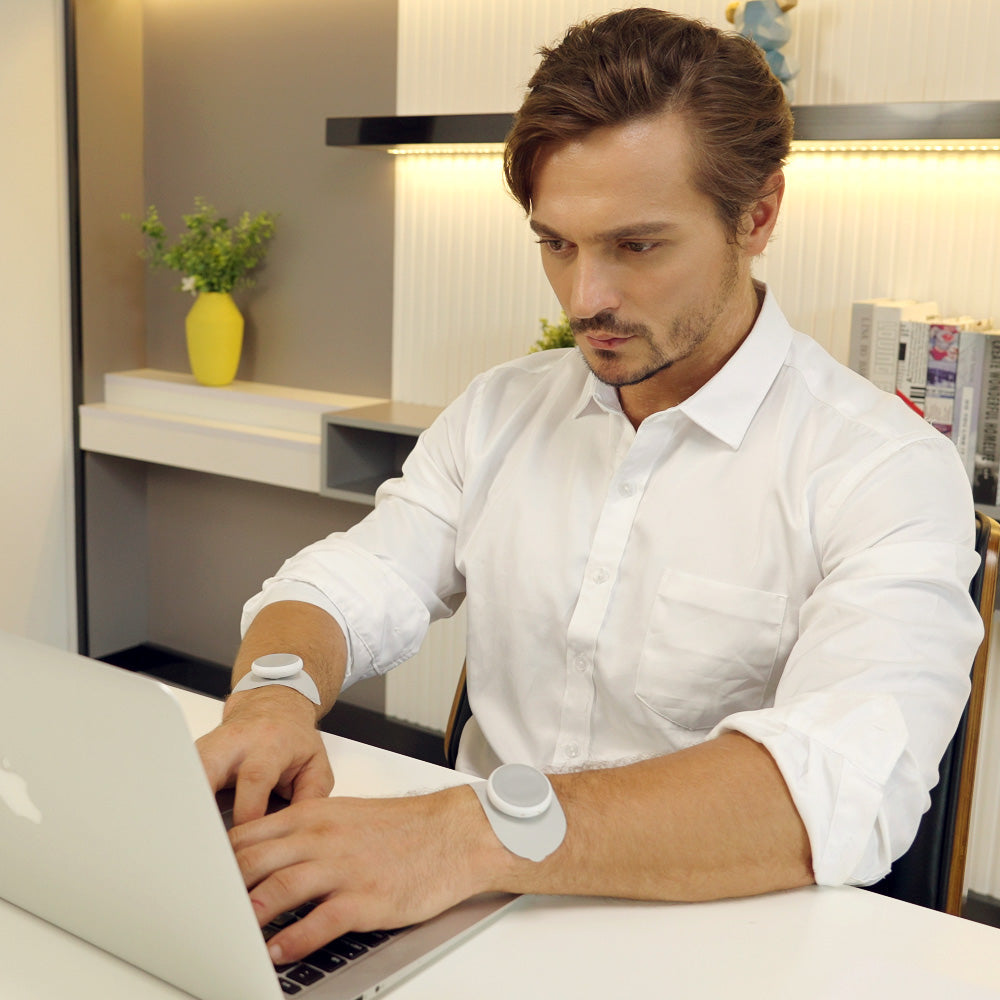
ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: What Is It & How It Can Help
Introduction:
Electrical Stimulation, commonly referred to as ES, is a therapeutic technique that utilizes controlled electrical currents to elicit physiological responses within the body. This article aims to provide an understanding of what electrical stimulation is, its various applications, and how it can offer substantial benefits in healthcare and rehabilitation.
Exploring Electrical Stimulation:
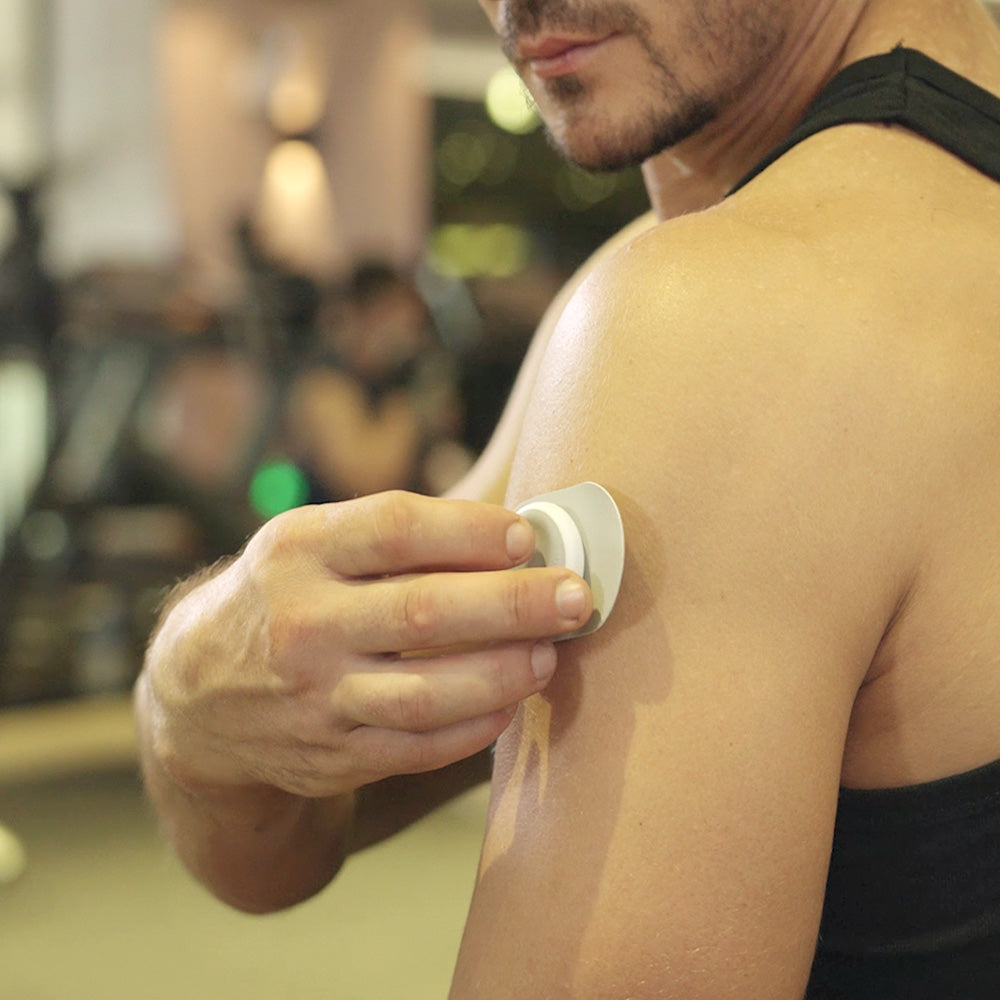
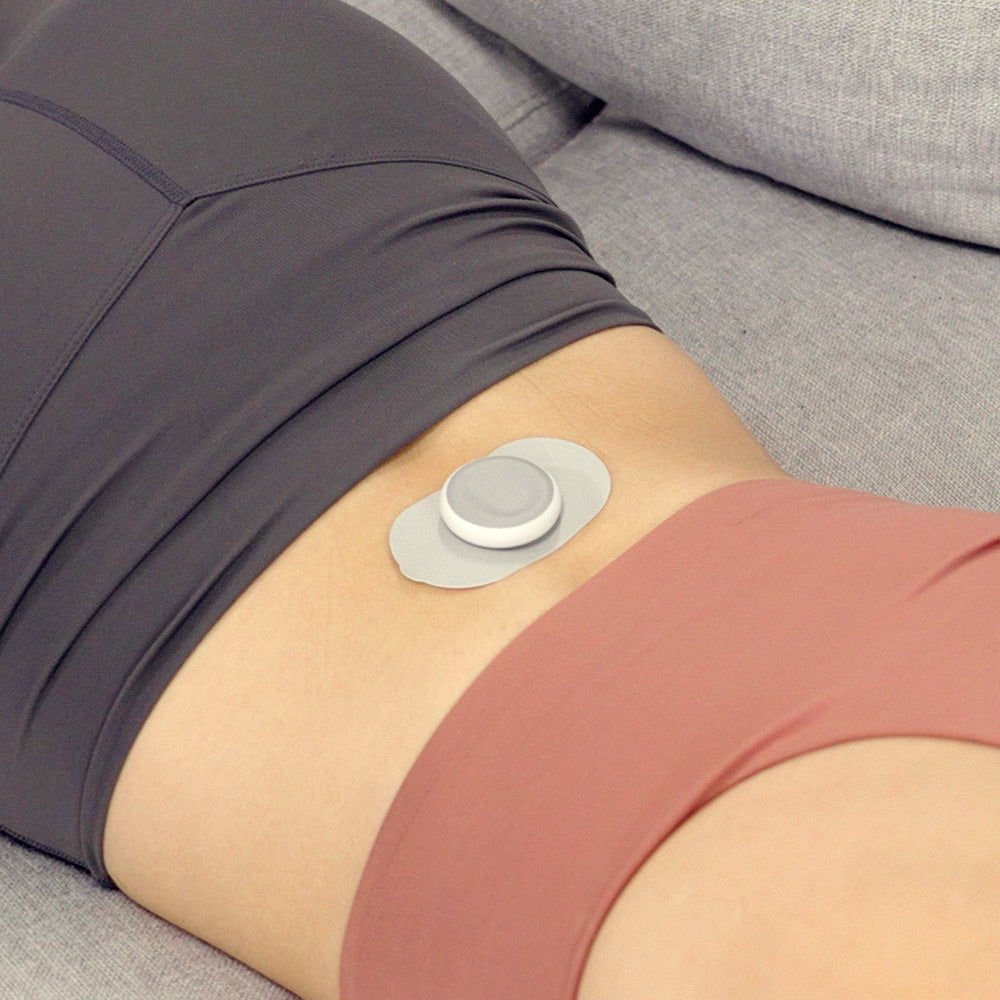
Electrical Stimulation involves the application of electrical currents to targeted areas of the body through electrodes. These currents can be used to achieve a range of therapeutic effects, including:
Muscle Activation: Electrical Stimulation can trigger muscle contractions, making it a valuable tool for maintaining muscle strength and preventing atrophy, especially in individuals with limited mobility.
Pain Management: Certain types of Electrical Stimulation, such as Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), work by altering nerve signals and promoting the release of natural pain-relieving endorphins.
Neurorehabilitation: Electrical Stimulation aids in re-educating the nervous system, helping patients regain proper movement patterns and coordination after injuries or surgeries.
Spasticity Reduction: By calming overactive nerve signals, Electrical Stimulation can effectively reduce muscle spasticity and promote relaxation.
Wound Healing: Electrical Stimulation Therapy (EST) is used to enhance tissue healing and regeneration, particularly in chronic wounds.
Nerve Activation: Electrical Stimulation can stimulate nerves, aiding in the restoration of their function, which is particularly useful for conditions like nerve injuries or facial paralysis.
Applications of Electrical Stimulation:
Physical Rehabilitation: Electrical Stimulation is integrated into rehabilitation programs to boost muscle function and facilitate recovery post-orthopedic surgeries, injuries, or neurological disorders.
Pain Management: Electrical Stimulation techniques like TENS are employed for managing both chronic and acute pain, providing an alternative or complementary approach to traditional pain relief methods.
Sports Performance: Athletes utilize Electrical Stimulation for muscle conditioning, strength enhancement, and injury prevention.
Neurological Conditions: Electrical Stimulation plays a pivotal role in treating conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, and multiple sclerosis, aiding in muscle re-education and improved mobility.
Urinary and Pelvic Health: Electrical Stimulation is leveraged to strengthen pelvic floor muscles and address issues like urinary incontinence.
Cosmetic and Aesthetic Uses: Electrical Stimulation-based treatments are applied for facial muscle toning, cellulite reduction, and skin rejuvenation.
Important Considerations When Using Electrical Stimulation:
Professional Supervision: It is crucial to administer Electrical Stimulation under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals or trained practitioners.
Personalization: Treatment parameters, including current intensity, frequency, and duration, should be tailored to suit individual needs and responses.