In joints, which provide us with movement ability, cartilages are what gives them flexibility. Degenerative processes like normal aging cause cartilage erosion, and often the first joint to suffer from this erosion is the knee. The result: osteoarthritis.
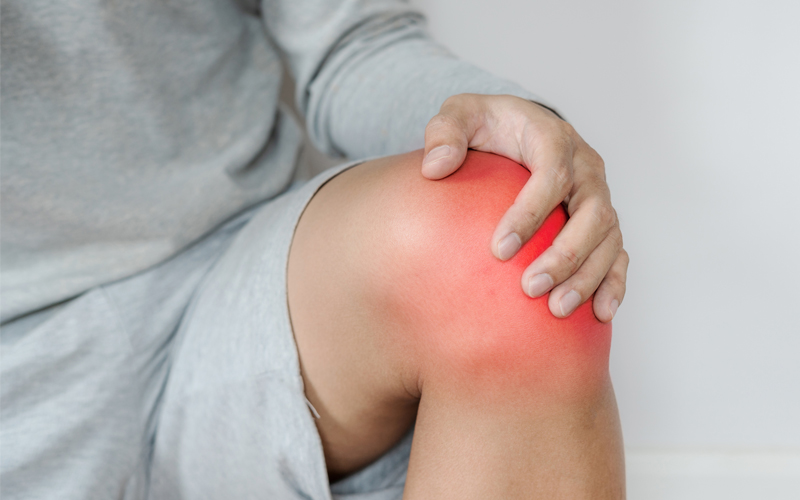
Joints connect two or more bones together, giving them the ability to move. At the end of every bone that reaches the joint, there is cartilage. Cartilages are connective tissues made up of proteins and other materials. The cartilages are characterized by dense fibers and flexibility thanks to their ability to absorb and disperse fluids within the joint.
Sometimes, due to degenerative processes in old age, the cartilages become eroded. This occurs in “accident-prone” joints that carry a lot of weight. For example, the hips, the wrists, and most importantly, the knees. The result: cartilage erosion that leads to osteoarthritis.
What causes osteoarthritis in the knee?
Due to cartilage erosion, direct bone friction is created, and this results in inflammation. This inflammation often leads to pain and limited mobility.
What do you feel when you have osteoarthritis in the knee?
The most common symptom of knee cartilage erosion is pain in the area, especially during movement or lifting. Sometimes, going from sitting to standing also involves intense pain. People with knee osteoarthritis may also feel pain even when they are not moving.
Along with the pain, stiffness appears in the joint and even creaking sounds as the bones meet with each other without proper cushioning of the cartilage. If there is a bout of inflammation, swelling, slight redness, and a localized heat sensation will also appear.
How is knee osteoarthritis diagnosed?
Along with the physical examination performed by your doctor, they may send you do get X-rays, which can indicate the changes in the cartilage structure of the knee. However, sometimes there are similar medical conditions that are not related to the pain of cartilage erosion.
How is knee osteoarthritis treated? Is there any advanced instrumentation that can help?
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, pain relief is possible. In most cases, the first course of treatment is physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles and ease some weight off the knee. Beyond strengthening your muscles, relieving pain, and “learning” proper movements, you may also need to lose weight, and so you can take off some of the load in the joint. If the pain is severe, painkillers and even injections may be used. Surgery is typically only offered as a last resort.
This is also an opportunity to try out advanced pain relief technologies at home, such as ““Olynvolt™ Pocket”,” a lightweight, simple, and user-friendly device.
How to avoid osteoarthritis pain?
Unlike what experts previously thought, moderate sports activity may actually be beneficial. Make sure to talk to your doctor to find out which exercise is right for you. Recommended activities include Pilates, swimming, walking, and more. It is also essential to maintain a proper body weight.